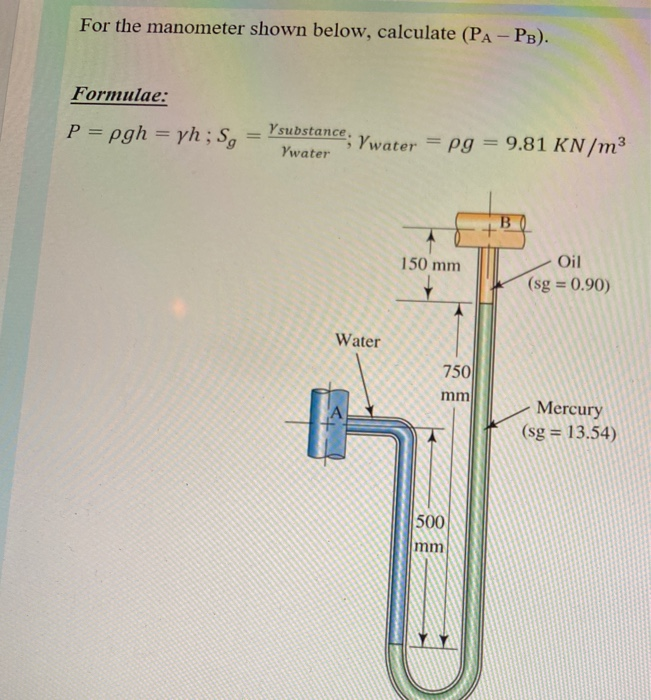
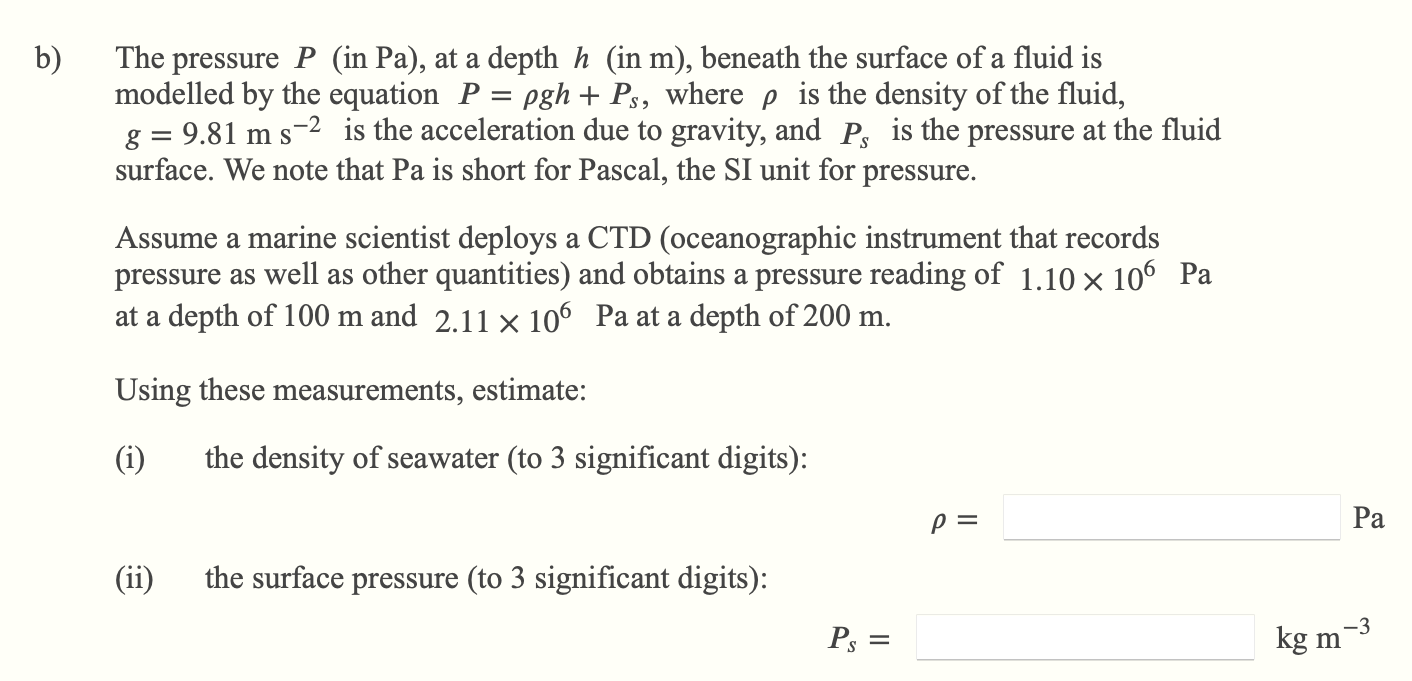
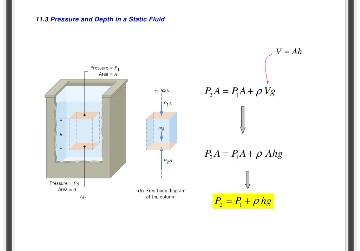
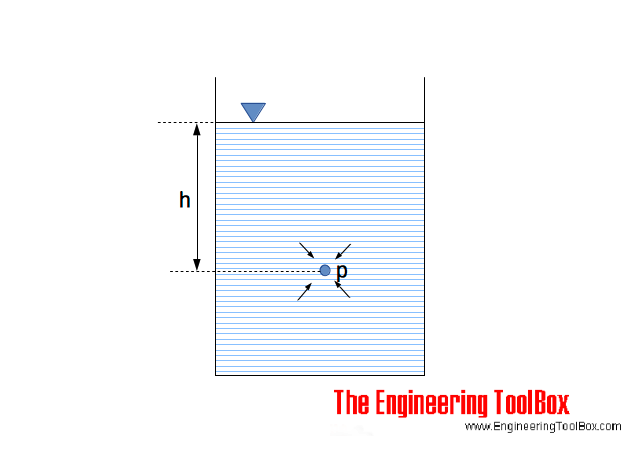
At a depth of 1000 m in an ocean (a) What is the absolute pressure? (b) What is the gauge pressure? (c) Find the force acting on the window of area 20
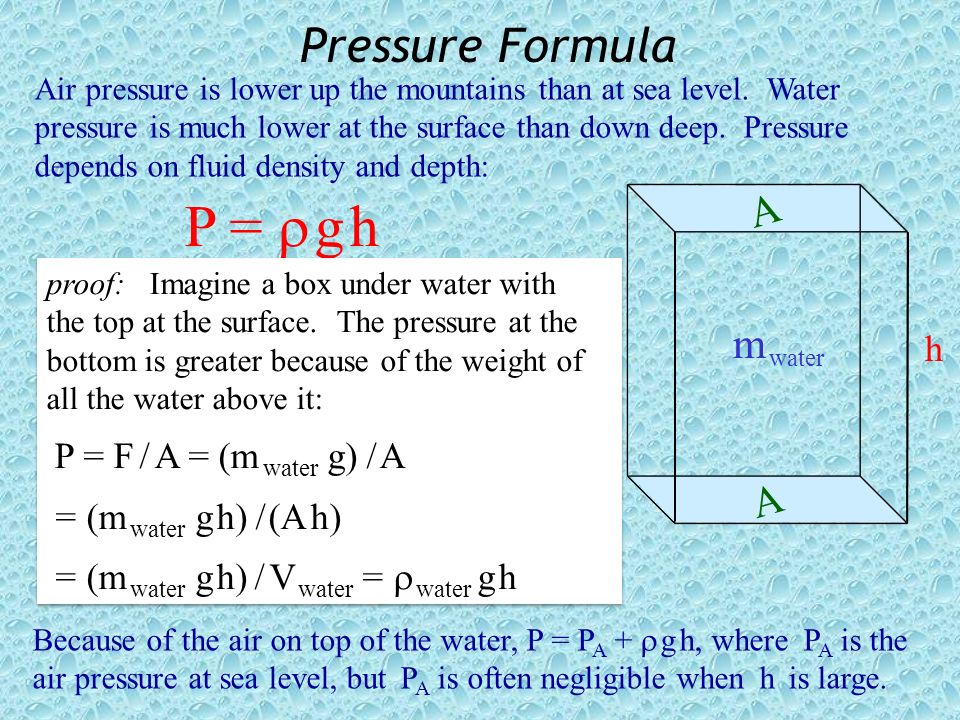
Calculating the pressure on the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid, how come it only depends on three variables? : r/AskPhysics
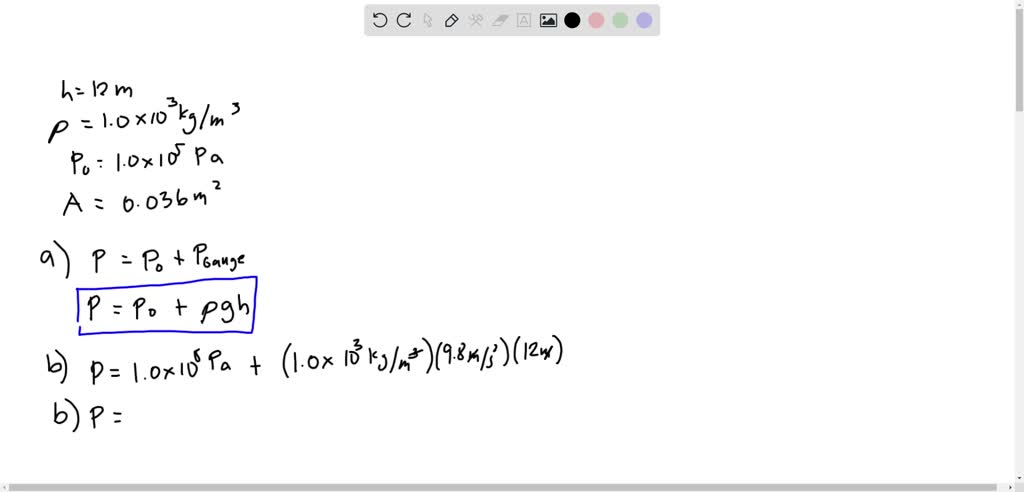
SOLVED: A person is diving in a lake in the depth of h = 12 m. The density of the water is ρ = 1.0 x103 kg/m3. The pressure of the atmosphere

SOLVED: The pressure Pis given as P = Po pgh and you measured the density p and depth h. Assume Po and g have negligibly small uncertainties so we do not consider
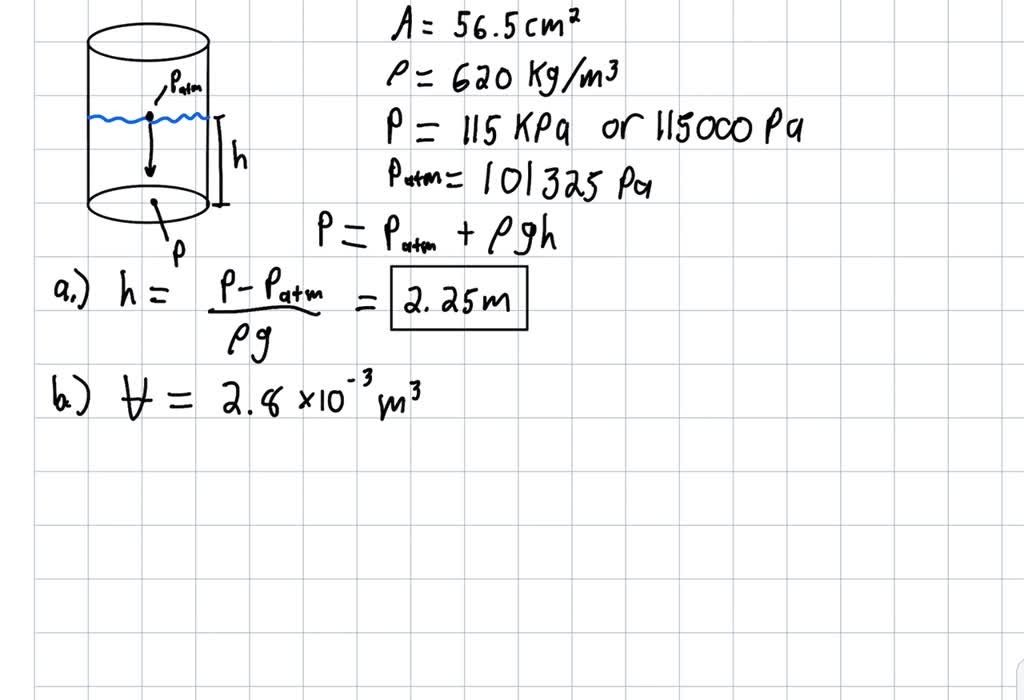
SOLVED: Use g = 9.8 m/s2. The pressure at the bottom of a cylindrical container with a cross-sectional area of 56.5 cm2 and holding a fluid of density 620 kg/m3 is 115

How to Find the Absolute Pressure in a Constant Density Fluid at a Certain Depth | Physics | Study.com

An open U tube contains two immiscible liquids of densities ρ1 and ρ2 (ρ1 > ρ2) as shown in figure. If PA, PB, PC and PD refer to the pressure at points